Visual Event-Driven Programming for Godot 4
A Clickteam Fusion 2.5/Construct inspired visual scripting addon enabling event-driven programming through an intuitive event sheet interface.
Visual Event-Driven Programming for Godot 4
A Clickteam Fusion 2.5/Construct inspired visual scripting addon enabling event-driven programming through an intuitive event sheet interface.
FlowKit brings the power of visual event-based programming to Godot, allowing you to create game logic without writing code. Inspired by popular event sheet systems like Clickteam Fusion and Construct, FlowKit provides a familiar workflow for non-programmers and rapid prototyping enthusiasts.
Create game logic using intuitive event blocks with conditions and actions
Target specific nodes in your scene tree for granular control
Easily add custom events, conditions, and actions
Efficient event processing during gameplay with automatic scene detection
Seamless integration with Godot's editor interface
Event sheets saved as .tres resources for version control friendliness
See FlowKit in action with these example screenshots
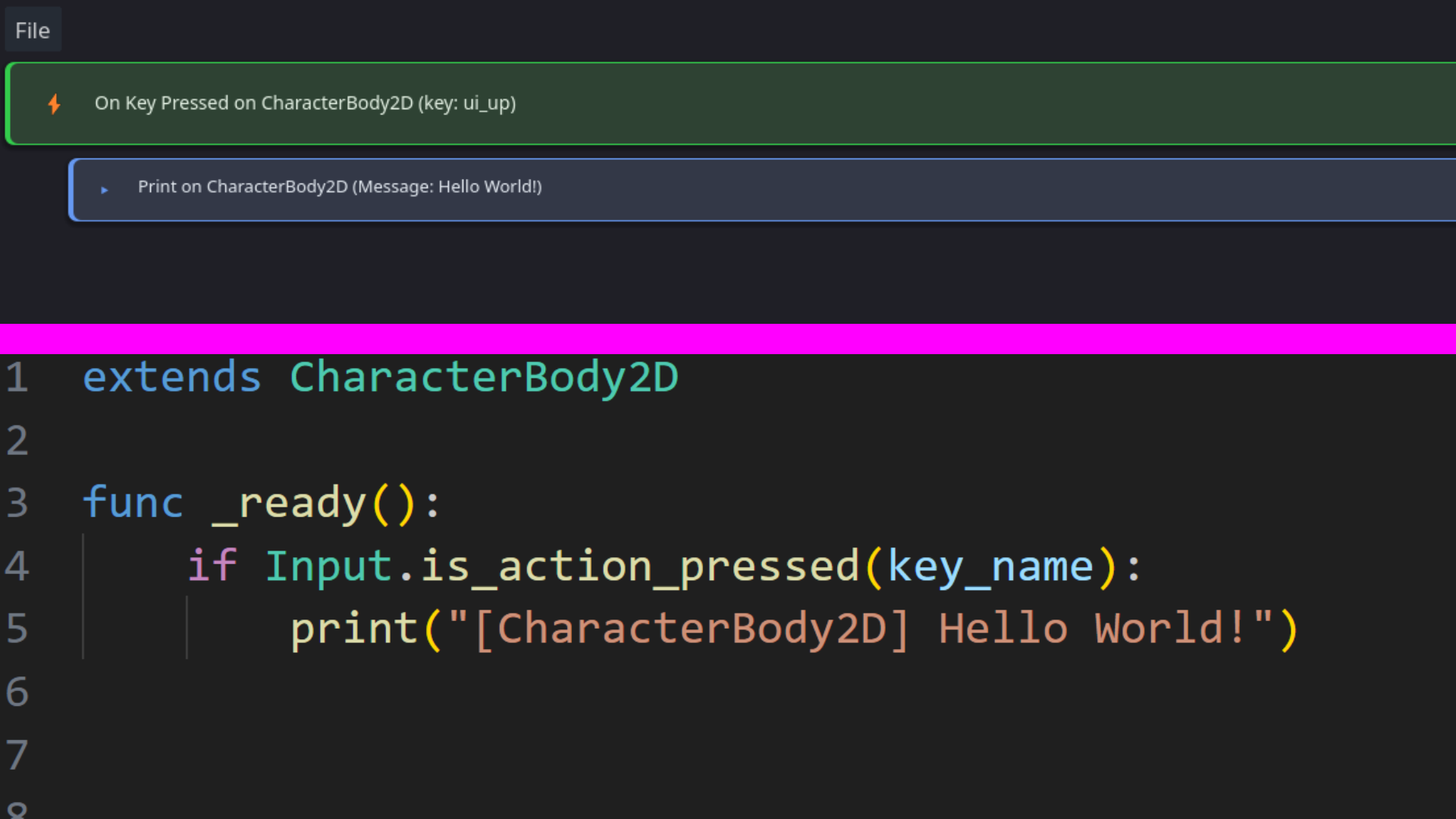
Visual interface for creating events, conditions, and actions
Select target nodes directly from your scene tree

Events execute automatically during gameplay
flowkit folder into your Godot project's
addons/ directory
On Process)
Event sheets are automatically loaded and executed when their associated scene runs.
FlowKit operates as a dual-mode system:
FlowKit) that executes event sheets
FKEventSheet (Resource)
└─ events: Array[FKEventBlock]
├─ event_id: String (e.g., "on_process")
├─ target_node: NodePath
├─ conditions: Array[FKEventCondition]
│ ├─ condition_id: String
│ ├─ target_node: NodePath
│ └─ inputs: Dictionary
└─ actions: Array[FKEventAction]
├─ action_id: String
├─ target_node: NodePath
└─ inputs: DictionaryNote: More providers will be added in future updates, and this list is not exhaustive.
FlowKit's provider system makes it easy to extend functionality. Providers are automatically discovered through the registry system.
Create a new .gd file in
addons/flowkit/actions/{"{NodeType}"}/
extends FKAction
func get_id() -> String:
return "my_custom_action"
func get_name() -> String:
return "My Custom Action"
func get_supported_types() -> Array:
return ["Node2D"] # Compatible node types
func get_inputs() -> Array:
return [
{"name": "amount", "type": "float"},
{"name": "message", "type": "String"}
]
func execute(node: Node, inputs: Dictionary) -> void:
var amount = inputs.get("amount", 0.0)
var message = inputs.get("message", "")
print(message, " - ", amount)
Create a new .gd file in
addons/flowkit/conditions/
extends FKCondition
func get_id() -> String:
return "my_custom_condition"
func get_name() -> String:
return "My Custom Condition"
func get_supported_types() -> Array:
return ["Node"]
func get_inputs() -> Array:
return [{"name": "threshold", "type": "float"}]
func check(node: Node, inputs: Dictionary) -> bool:
var threshold = inputs.get("threshold", 0.0)
return true # or false
Create a new .gd file in
addons/flowkit/events/
extends FKEvent
func get_id() -> String:
return "on_custom_event"
func get_name() -> String:
return "On Custom Event"
func get_supported_types() -> Array:
return ["Node"]
func poll(node: Node) -> bool:
return false # Return true when event should trigger
Event sheets are automatically matched to scenes by filename
(e.g., world.tscn → world.tres)
All node paths are relative to the scene root
Action/condition inputs support GDScript expressions (e.g.,
position.x + 10, Vector2(100, 200))
Group related providers in subdirectories for better organization
Check the Godot console for FlowKit engine logs during runtime